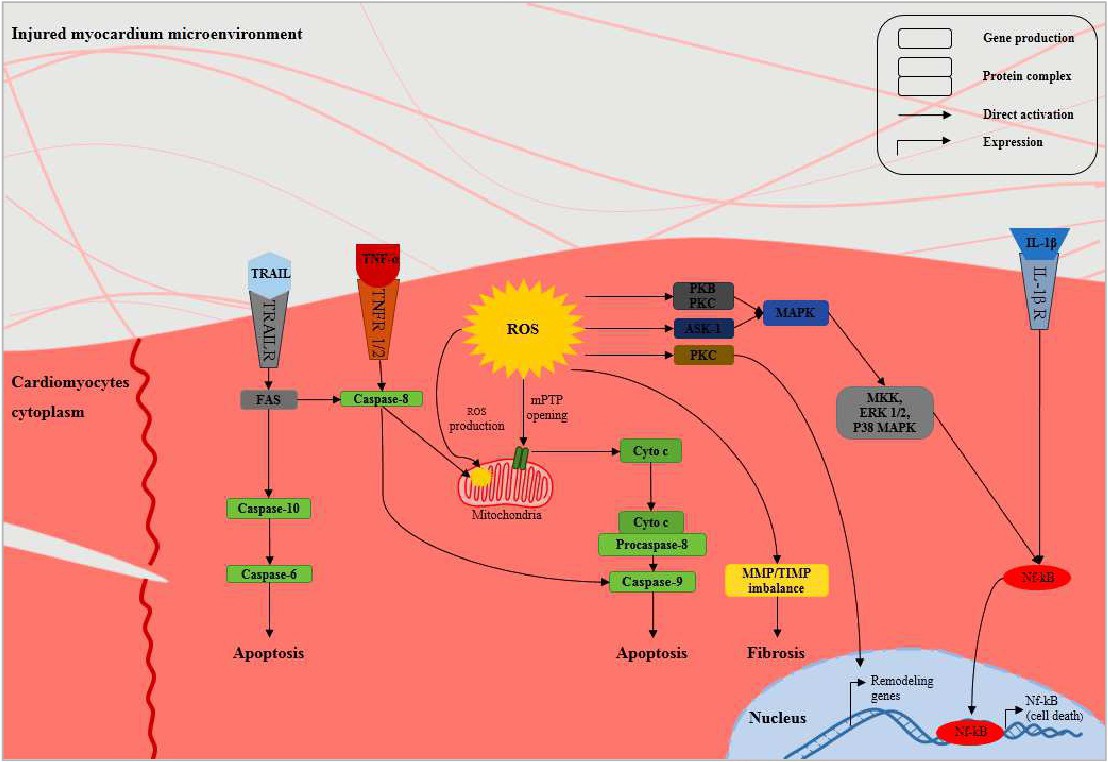
Fig. 4. A schematic representation of the cellular and molecular mechanisms of the cardiomyocytes death through the heart injury. Endogenic ROS production acquires early after injuries. Cytoplasmic ROS via changes mPTPs opening on the surface of mitochondria, releases of the cyto c into the cytoplasm, and activation and intra nucleus accumulation of Nf-kB through MAPK signaling stimulation leading to the cardiomyocyte apoptosis and necrosis. Beside, stimulation of the TNF-R1/2, IL-1R, and TRAIL-R as the death ligands by activation of the caspases cascades have a central role in developing the myocardium injuries. Abbreviations: Cyt-C: cytochrome -C, ERK: extracellular signal-regulated kinases, Fas: apoptosis antigen 1 (APO-1 or APT), IL-1R: interleukin-1 receptor, IL-1β: interleukin-1 β , MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase, NFκB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells , ROS: reactive oxygen spices, SCs: stem cells, TNF-R: tumor necrosis factor receptor, TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor- α, TRAIL: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, and TRAIL-R: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing receptor.